Welcome to digital publishing at Getty Publications!
This page will get you set-up with the essential tools you’ll need before diving into working in project created with Quire, our free and open source digital publishing tool.
We communicate via Slack and share documents via Google Drive. To start out, please sign up for them. If you haven’t used them before, take a little time to learn more about them on Getty GO.
Slack: Create an account with your getty.edu email address at https://thegetty.slack.com. Join the #pubs channel for sure, and check out others that might interest you, we’d recommend the #diversity channel, and for a great opportunity for one-on-one meetups with other Getty staff, check out the Donut meetups in the #virtual_coffee channel. And for fun, #pets-of-the-getty and #nomnom!
Google Drive: Email the Getty Digital Help Desk at GettyDigitalHelp@getty.edu and request a GSuite Account. Once you’ve got it, you can access it at https://drive.google.com/a/getty.edu.
Learn more about Slack and GSuite on Getty GO.
Most of the work we do centers around Quire, the digital publishing tool we built and use. Quire is designed to output books in multiple formats, with the online/website edition being the primary one. Along with the online version, Quire outputs e-books and PDFs (which we use to create print editions). To familiarize yourself with it, please peruse the Quire website: https://quire.getty.edu. You can also check out Getty publications built with Quire: https://www.getty.edu/publications/digital/digitalpubs.html; and Quire publications published by the community: https://quire.getty.edu/community/community-showcase/.
Documentation for Quire (the instructions on what it does and how to use it) can be found at https://quire.getty.edu/docs-v1/. You don’t need to read them all now but feel free to skim and take notes if you come across any issues or have any ideas that would make them better. You can also check out the Videos and Articles section of the documentation: https://quire.getty.edu/resources/articles-videos/, which includes a short demo and presentations by Greg, Erin, and some of our community members.
In the meantime, let’s get you up and running.
1. Join GitHub
While Quire is the tool we use for making books, GitHub is the tool we use to manage that process and manage Quire. So first, you’ll need to sign up for a GitHub account at https://github.com/join, following Getty’s account guidelines.
Getty GitHub Account Guidelines:
-
Add your real name and a profile picture at https://github.com/settings/profile (Getty Digital prefers but does not require that it is an actual picture of you)
-
Update your email notifications to go to your getty.edu email account if they don’t already at https://github.com/settings/emails
-
Set up two-factor authentication at https://github.com/settings/security (further instructions at https://help.github.com/en/articles/configuring-two-factor-authentication)
Once you have your account, let Greg know your username, and he’ll add you to Getty’s organizational team on GitHub, at which point you’ll be able to access Quire and all of our digital publications. You’ll also have access to the Quire community forum: https://github.com/thegetty/quire/discussions.
2. Learn About the Command Line
While we are getting you set up as part of the GitHub organizational team, take some time to learn about the command line, which is a text-based interface for navigating a computer and running command-line scripts and software, like Quire.
Start with the opening part of the Quire Tutorial, and then check out the “Really Friendly Command Line Intro” if you want to learn more.
3. Install Node Version Manager (nvm)
Quire uses a tool called Node.js, and nvm is a tool to manage different versions of Node.js. Older Quire projects need older versions of Node.js and so it is useful to install nvm. The full installation instructions are here: https://github.com/nvm-sh/nvm. But this condensed version should cover the basics.
-
Install the nvm script with the following command in your command-line shell:
curl -o- https://raw.githubusercontent.com/nvm-sh/nvm/v0.40.0/install.sh | bash -
Verify with this command, which should return
nvm. If it does not, see the Troubleshooting info at https://github.com/nvm-sh/nvm#troubleshooting-on-macos.command -v nvm -
Install the two versions of node you will need:
nvm install 14.18.1nvm install 18.16.0 -
Optionally, set a default version to use with
nvm alias default 18.16.0. This default will be the one used every time you open a new Terminal window. -
To choose/change a Node version to run use
nvm use 14ornvm use 18. This will be the version used for as long as that Terminal window is open, or until you change it again.
4. Install Quire
Once you have installed nvm and the two version of node (14
and 18), you can now install Quire. More precisely, you will
be installing the Quire Command-Line Interface (or CLI), which
is the tool you use to run Quire commands. You will be
installing the latest version of the Quire CLI with Node 18,
and the older version with Node 14. In each case, start by
using nvm to switch Node versions and then run the
corresponding npm install command as noted below.
nvm use 18
npm install --global @thegetty/quire-cli
nvm use 14
npm install --global @thegetty/quire-cli@0.20.4
The addition of @0.20.4 in this command installs
version 0.20.4 of the Quire CLI. This version is
used for the on the Quire docs website, as well as a number of
older Quire projects. To switch between Quire versions, you
can use nvm use 18 or
nvm use 14 before running any Quire commands.
Switching versions of Node, will automatically switch versions
of Quire.
To confirm your installation, run
quire --version in your Terminal. It should
return a version number. If it does, switch to your other
version of Node with the nvm use command, and run
the --version command again. It should return a
different version number this time. If version numbers were
returned each time, you’re all set and can proceed to the next
step. If not, check in with the digital team to help
troubleshoot the installation.
5. Learn More About Visual Studio Code
A text editor is used to add and edit content in a Quire publication. Content is stored as plain text files that are primarily written in Markdown & YAML. All computers have basic text editors preinstalled, but we recommend using Visual Studio Code (VS Code) which offers a number of very useful features.
⬇️ Download and install Visual Studio Code: https://code.visualstudio.com/
To learn more about VS Code, watch these two short introductory videos and check out the VS Code page of this guide for some tips and tricks we‘ve found useful.
-
Learn Visual Studio Code in 7min (7:16): The official beginner Tutorial
-
Get started with Visual Studio Code (5:03): An older introduction, but with some useful framing
6. Complete the Quire Tutorial
Now that you have installed nvm, Quire, and Visual Studio Code, you can proceed with the Quire step-by-step tutorial. Start with step 3. Create a New Project.
If there is anything unclear or confusing in the tutorial, please take notes and share your observations with Erin once you are done, we are always looking for ways to improve our documentation and training materials for the Quire community!
7. Learn More About GitHub
As mentioned above, we use GitHub to manage all of our digital publications. GitHub keeps our files, manages them with version control (what’s changed and when), lets us collaborate on projects, track issues, and share them with others once they’re published.
Read through the GitHub guide on the Quire website. Don’t worry if it doesn’t all make sense immediately, you will have plenty of opportunities to learn through practice and use.
We also highly recommend watching the Git and GitHub for Poets video series (particularly the first six episodes) to better acquaint yourself with the hows and whys of GitHub.
As you’ll learn, GitHub can be accessed online, through the command line, or with GitHub Desktop. which is what we use at Getty.
⬇️ Download and install GitHub Desktop: https://desktop.github.com/
When you have time or if you are interested in learning more about GitHub, feel free to take a deeper dive by checking out the GH Desktop documentation https://help.github.com/en/desktop.
8. Install an SSH Key
SSH is short for Secure Shell. It is a communication protocol used (in this case) between GitHub and your computer that is more secure than the HTTP protocol GitHub otherwise uses by default.
Many Getty Quire projects use SSH as a way of securing third-party licensed images that we store on GitHub but don’t want publicly accessible. When cloning one of these projects, an SSH key gives you permission to access the private image repository and pull those images into your project.
Follow these instructions on Github.com to set up your SSH key:
- Check for existing SSH keys
- Generate a a new key and add it to the SSH agent
- Add the new key to your GitHub account
Files that start with a period, like the
.ssh file, are automatically hidden in macOS
Finder. To make them visible press Command+Shift+. (period).
Here is an example of correctly setting up your SSH key using Terminal:
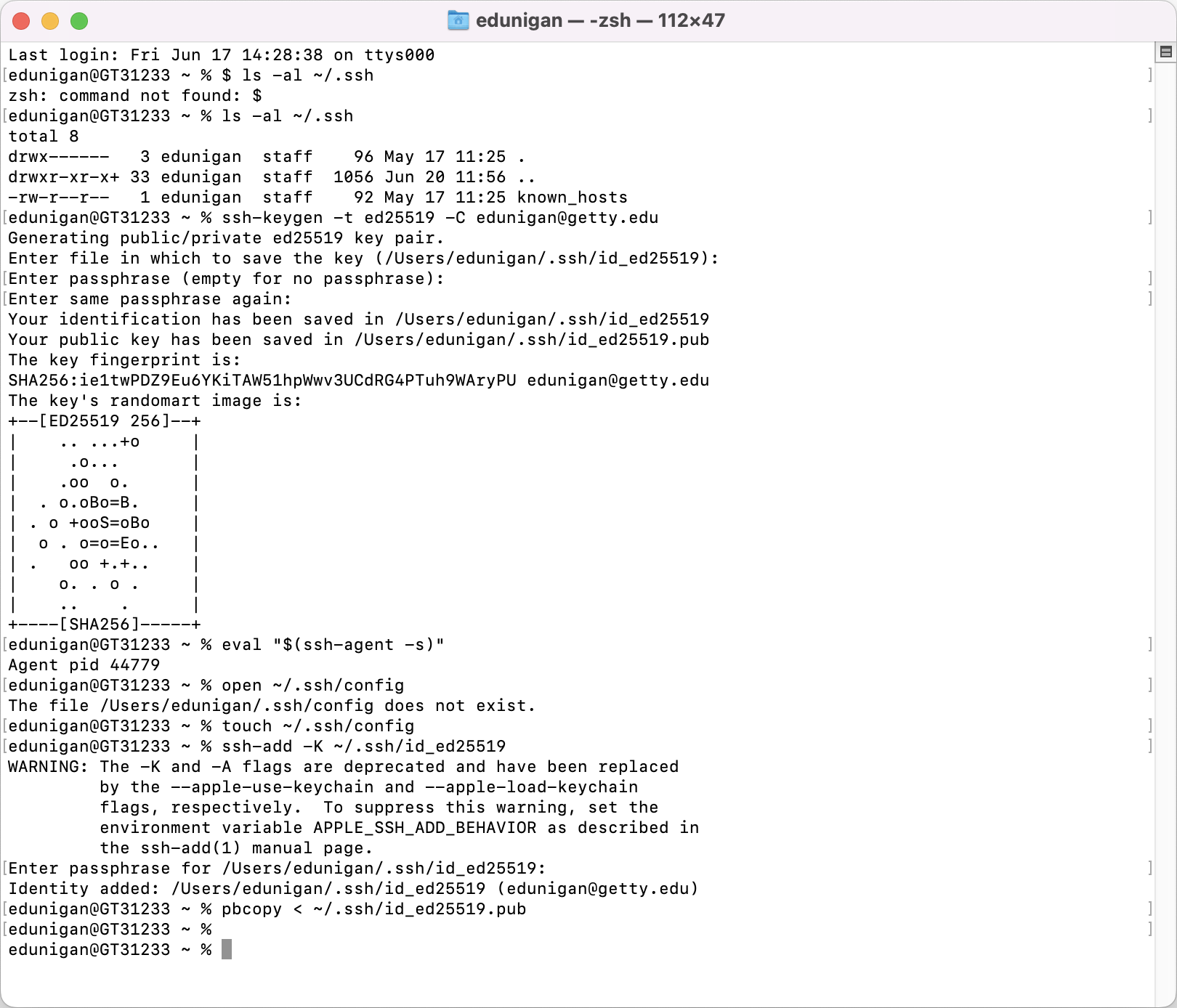
9. Install Git LFS
Follow the instructions in the GitHub Docs to install Git LFS.
(LFS stands for Large File Storage and is a way that particularly large files like high-resolution images and press-ready PDFs are managed in git. Most of Getty’s Quire projects use Git LFS.)
10. Make Your First Project Contribution with GitHub
Once you’ve spent some time learning about Quire and GitHub,
you’ll be ready to make your first contribution to the Quire
website and documentation. When ready, please touch base with
Erin. Erin will help you get set-up with the
Quire-Docs repository, make sure you are using the correct version of Node, and
show how to choose
“good first issue”
to tackle.
Once you have choosen an issue, read through the CONTRIBUTING.md file. This will provide all the instructions needed to make a contribution to the website and documentation through GitHub.
You’ll continue to use GitHub throughout your time working on various Quire projects, whether in developing Quire itself or working on your own Quire project. It’s important to have a clear understanding of the process, so don’t hesitate to ask us any questions along the way.
Other Digital Publishing Projects & Tools
Aside from Quire, there are a few other projects that we’re involved in and a few other tools we use. These may or may not come up in your course of work, but they’re listed here as an FYI. If you’re ever interested in learning more about any of these, please let us know.
-
The Virtual Library: Launched in 2014, the Virtual Library (the VL) hosts full-text PDF of 300+ Getty books for free download and online reading. We add a handful of new titles every year.
-
Getty Website: We manage Publications’ presence on getty.edu, which is currently undergoing a major redesign of both the front-end design and the back-end architecture.
-
Consonance: This is our title management system which was implemented in 2020/21. It holds key metadata on all our books, and as we grow into it, will be a place where we track schedules, and other workflow items. Maureen Winter can get you an account when/if you need it.
-
OTMM: Open Text Media Management (OTMM) is Getty’s primary digital asset management system. It contains much of the collection and marketing/press images and we often will do research and such for book projects there. Publications is just starting to use it more for storing book cover files and other key assets.
-
Jira: Jira is the project- and issue-tracking tool Getty Digital uses to manage its work, and so we use it when working with them on Quire or other projects. It’s much like GitHub issues but on an enterprise level.
-
IIIF: The International Image Interoperability Framework (IIIF, which people say as “Triple I F”) is a standard way of storing, delivering and viewing high-resolution images across institutions. The Getty is a founding member of the IIIF consortium, and Quire makes use of it in a growing number of ways.
-
Netlify: A web-hosting service that we use for all of our Quire projects and that we often recommend for others using Quire. Netlify can build directly from GitHub repositories, and this allows us to use it for site previews during development, as well as for hosting the final versions.
-
EPUB: Getty Publications also puts out an increasing number of ebook editions of our print books in EPUB and PDF formats. This work is handled primarily by the Sales & Marketing department and Production. EPUB in particular is the primary universal e-book format so it is a very important format for digital publishing broadly, and is worth learning more about if you’re interested in pursuing digital publishing work outside the Getty.
There are a number of organizations, conferences, etc. that we are affiliated with or participate in and that may be of interest to you: